
| Taxa: |
| Order: |
| Family: |
| Aves |
| Passeriformes |
| Parulidae |
| NatureServe Global Rank: |
| NatureServe State (NC) Rank: |
| G5 |
| S5B,S4N |
| Federal Status: |
| NC State Status: |
| --- |
| --- |
| Land Unit |
| US Fish & Wildlife Service |
| US Forest Service |
| US National Park Service |
| US Department of Defense |
| NC State Parks |
| NC University System |
| NC Wildlife Res. Com. |
| NC Forest Service |
| NC Div. of Coastal Mgmt. |
| Local Governments |
| Non-Governmental Org. |
| Other Public Lands |
| Private Lands |
| GAP Status 1-2 |
| All Protected Lands |
| Statewide |
| Hectares |
| 128,682.54 |
| 126,493.65 |
| 84,894.84 |
| 24,324.75 |
| 24,253.56 |
| 27,243.90 |
| 86,075.73 |
| 9,959.25 |
| 8,956.53 |
| 2,794.32 |
| 25,911.99 |
| 1,227.33 |
| 2,968,209.27 |
| 294,282.66 |
| 547,086.36 |
| 3,519,027.66 |
| Acres |
| 317,981.42 |
| 312,572.56 |
| 209,779.68 |
| 60,107.75 |
| 59,931.84 |
| 67,321.13 |
| 212,697.72 |
| 25,644.57 |
| 22,132.06 |
| 6,904.91 |
| 64,029.91 |
| 3,032.80 |
| 7,334,603.41 |
| 728,222.88 |
| 1,352,914.30 |
| 8,696,739.76 |
| % of Dist. on |
| Prot. Lands |
| 23.5 % |
| 23.1 % |
| 15.0 % |
| 4.4 % |
| 4.4 % |
| 5.0 % |
| 15.7 % |
| 1.8 % |
| 1.6 % |
| 4.7 % |
| 4.7 % |
| 0.1 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 53.8 % |
| ----- |
| ----- |
| % of Dist. on |
| All Lands |
| 3.7 % |
| 3.6 % |
| 2.4 % |
| 0.7 % |
| 0.7 % |
| 0.8 % |
| 2.4 % |
| 0.3 % |
| 0.3 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 0.7 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 84.3 % |
| 8.4 % |
| ----- |
| ----- |
|
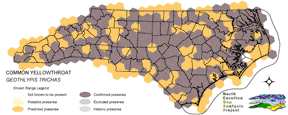
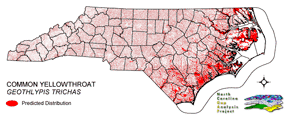
Breeds across the state and into the barrier islands, with the largest numbers near the coast and fewer in the high elevations of the mountains (Fussell 1994, Fussell and Lyons 1990, Potter et al. 1980). Commonly found in the dense vegetation surrounding sloughs and islands, along the edges of swamps and creeks (Griscom and Sprunt 1957), and in bogs (Dunn and Garrett 1997). On the coastal plain, breeds in salt (Ehrlich et al. 1988), fresh, and brackish marshes, wet shrub thickets, and pocosins (Fussell 1994). Also found in the dense early successional growth (Nicholson 1997) of drier habitats such as open forests (Dunn and Garrett 1997), brushy fields, hedgerows, thickets, (Potter et al. 1980), stream borders, woodland openings (Simpson 1992) and edges (Ehrlich et al. 1988). At high elevations, usually found along streams bordered by deciduous shrubs (Alsop 1991). Nest is built in a clump of grass, sedges, or reeds (Nicholson 1997) very close to the ground or the surface of water and concealed in bushes, grasses or reeds (Potter et al. 1980), which often form a canopy over the nest (Nicholson 1997). Insects are gleaned low in the vegetation or in damp ground or mud. After breeding, may forage higher in shrubs and small trees (Dunn and Garrett 1997). NATURE SERVE GLOBAL HABITAT COMMENTS: Marshes (especially cattail), thickets near water, bogs, brushy pastures, old fields, and, locally, undergrowth of humid forest. In migration and winter also in brushy and shrubby areas in both moist and arid regions (AOU 1983). Nests just above ground or over water, in weeds, reeds, cattails, tules, grass tussocks, brier bushes, and similar situations; often at base of shrub or sapling, sometimes higher in weeds or shrubs up to about 1 m. |
| Code | Name | Description | NC Natural Heritage Program Equivalent |
| 3 | Tidal Marsh | Fresh and brackish tidal marshes, including cord grass, wild rice, sawgrass and needlerush alliances. | Brackish Marsh, Interdune pond, Maritime wet grassland |
| 124 | Maritime Scrubs and Tidal Shrublands | Coastal shrubs including wax-myrtle, swamp rose, alder, yaupon, and greenbriar. | Maritime Shrubs, Salt Shrub |
| 75 | Tidal Swamp Forest | Swamp tupelo dominated forest with or without black tupelo and/or cypress trees. Restricted to the tidal zones in the coastal plain. May have inclusions of coastal red cedar woodlands. | Tidal cypress - gum swamp |
| 121 | Maritime Pinelands | Loblolly forests and woodlands of the outer coastal plain. | Estuarine Fringe Loblolly Pine Forest |
| 17 | Maritime Forests and Hammocks | Maritime forests and woodlands dominated by live or sand laurel oak. Estuarine Fringe forests dominated by loblolly pine. | Coastal Fringe Evergreen Forest, Maritime Deciduous Forest, Maritime Deciduous Forest |
| 126 | Interdune Wooded Depression Swamp | Includes swamps dominated by sweetbay and swampbay or dogwood dominated forests. | Maritime Shrub Swamp, Maritime Swamp Forest |
| 380 | Coastal Plain Fresh Water Emergent | Emergent vegetation in fresh water seepage bogs, ponds and riverbeds of the coastal plain. Includes alliances dominated by sedges, eelgrass, as well as cane found in unforested cane-brakes. | Small Depression Pond, Sandhill Seep, Floodplain Pool, Unforested Floodplain Canebrake, Riverscour Prairies, Vernal Pools |
| 173 | Coastal Plain Riverbank Shrubs | Shrub dominated riverbanks, commonly dominated by willows and/or alders. | Sand and Mud Bar |
| 50 | Coastal Plain Mixed Bottomland Forests | Includes forests dominated by a variety of hardwood species, including sweetgum, cottonwood, red maple. | Coastal Plain Bottomland Hardwood (in part), Coastal Plain Levee Forest |
| 49 | Coastal Plain Oak Bottomland Forest | Bottomland forests dominated by deciduous oak alliances. Oaks represented can include swamp chestnut, cherrybark, willow, and/or overcup oak. Inclusions of loblolly pine temporarily flooded forests occur in patches. Hydrology is temporarily to seasonally flooded. | Coastal Plain Bottomland Hardwoods (in part) blackwater subtype, brownwater subtype |
| 158 | Coastal Plain Nonriverine Wet Flat Forests | Loblolly pine - Atlantic white-cedar - red maple - swamp tupelo saturated forests as well as forests dominated by loblolly, sweetgum, and red maple in non-riverine flats. | Non-riverine Wet Hardwood Forest |
| 41 | Peatland Atlantic White-Cedar Forest | Dense stands of Atlantic white cedar with saturated hydrology. Can include swamp tupelo, red maple, and pond pines with a moderate shrub and herb layer. | Peatland Atlantic White-Cedar Forest |
| 15 | Seepage and Streamhead Swamps | Includes extensive peat flats in the coastal plain, dominated by swamp tupelo, maples, and Atlantic white cedar alliances. In the sandhills includes streamhead pond pine and bay forests alliances. Saturated hydrology. | Bay Forest, Small Depression Pocosin, Streamhead Atlantic White Cedar Forest, Streamhead Pocosins |
| 30 | Cypress-Gum Floodplain Forests | Swamps dominated by black or swamp tupelo with or without Taxodium. Seasonally to semi-permanently flooded hydrology. | Cypress-Gum Swamps |
| 78 | Pond-Cypress - Gum Swamps, Savannas and Lakeshores | Cypress dominated swamps and lakeshores. Can include bays dominated by pond cypress or shorelines of coastal plain lakes with a narrow band of cypress. | Non-riverine Swamp Forest, Natural Lakeshores (in part) |
| 385 | Oak Bottomland Forest and Swamp Forest | The swamp chestnut oak, cherrybark oak, shumard oak and sweetgum alliance is one representative. Other alliances are dominated by water, willow, and overcup oaks. Swamp forests can be dominated by sweetgum, red maple, and black gum being dominant. Loblolly can occur in combination with sweetgum and red maple, or with tulip poplar. Includes saturated and semi- to permanently flooded forests in the mountains. | Piedmont/Mountain Bottomland Forest, Piedmont/Mountain Swamp Forest |
| 63 | Coastal Plain Mesic Hardwood Forests | Beech dominated forests with white oak and northern red oak as possible co-dominants. Dry-mesic to mesic forests on slopes and small stream bottoms in the coastal plain. | Mesic Mixed Hardwood Forest, Basic Mesic Forests |
| 138 | Coastal Plain Dry to Dry-Mesic Oak Forests | Oak dominated forests of the coastal plain. Includes white oak forests with water oak or northern red oak and hickories as co-dominants. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Basic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 87 | Pocosin Woodlands and Shrublands | Includes pond pine woodland, low pocosin and high pocosin shrub dominated areas. Canebrakes and bay forests may be present. | Pond Pine Woodlands, Peatland Canebrake, Small Depression Pocosin |
| 67 | Wet Longleaf or Slash Pine Savanna | Wet flatwoods and pine savannas, typically dominated by longleaf pines, but slash or pond pines may be the dominant pines. | Wet Pine Flatwoods |
| 97 | Mesic Longleaf Pine | Longleaf pine woodlands without a major scrub oak component. Slash or loblolly pines may be present as well. | Mesic Pine Flatwoods |
| 42 | Xeric Longleaf Pine | Sandhills including a range of longleaf pine density from predominantly wiregrass, scrub oak dominated to true longleaf pine woodland. This does not include mesic or saturated flatwood types. | Xeric Sandhill Scrub, Pine/Scrub Oak Sandhill, Coastal Fringe Sandhill |
| 46 | Xeric Oak - Pine Forests | Mixed forest dominated by yellow pines with white or northern red oaks co-dominating. | Pine Oak Heath |
| 232 | Xeric Pine-Hardwood Woodlands and Forests | Mixed forest dominated by yellow pines with drier oaks including southern red, post, and chestnut oaks. | Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 239 | Piedmont/Mountain Emergent Vegetation | Emergent vegetation of all wetland hydrologies. Sites would commonly support species such as tussock sedge, rushs, and cattail alliances. | Rocky Bar and Shore (in part) |
| 267 | Riverbank Shrublands | Riverside shrubs with temporarily flooded hydrologies. Found in the both the Mountains and Piedmont. Containing dominants such as smooth alder and a Carolina or black willows. | Sand and Mud Bar |
| 269 | Floodplain Wet Shrublands | Saturated shrublands of the Piedmont, includes buttonbush, swamp-loosestrife, decodon and alders. | Piedmont/mountain Semipermanent Impoundment |
| 230 | Piedmont Mesic Forest | American Beech - Red Oak - White Oak Forests. | Mesic Mixed Hardwood |
| 384 | Piedmont/Mountain Mixed Bottomland Hardwood Forests | Includes temporarily to seasonally forests dominated by hardwood species. Hardwoods include sweetgum, red maple, sycamore which co-occur in a mosaic of bottomland and levee positions. Includes alluvial hardwood forests in the mountains. Hemlock and white pine may occur as inclusions, but are generally mapped separately. | Piedmont/Mountain Alluvial Forest, Piedmont/Mountain Levee Forest |
| 383 | Piedmont Mixed Successional Forest | Generally loblolly mixed with successional hardwoods. Sweetgum, tulip poplar and red maple are common co-dominants in these successional forests. | No equivalent |
| 228 | Piedmont Dry-Mesic Oak and Hardwood Forests | Primarily oak dominated forests, white oak is often dominant, with co-dominants including . Also represented by sweetgum and tulip poplar dominated forests. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Basic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 222 | Piedmont Dry-Mesic Pine Forests | Loblolly dominated forests resulting from succession following clearing. This type occurs on all moisture regimes following disturbance with the exception of the extremely xeric sites. | No equivalent |
| 382 | Dry Mesic Oak Pine Forests | Mixed forests of the coastal plain and piedmont. Includes loblolly pine with white, southern red and/or post oak and loblolly with water oak. On basic sites of the piedmont, eastern red cedar may co-occur with post, black, and blackjack oaks. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Xeric Hard Pan Forest, Chestnut Oak Forest, Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 220 | Piedmont Xeric Pine Forests | Dry to xeric pine forests dominated by Virginia pine, shortleaf pine or Eastern Red Cedar. | Pine Oak Heath |
| 226 | Piedmont Xeric Woodlands | Generally post and blackjack oak dominated woodlands. White ash and pignut hickory can be found in combination with Eastern red cedar on glades. | Xeric Hardpan Forest |
| 20 | Coniferous Regeneration | Regenerating pine stands. Predominantly loblolly pine, but slash and longleaf stands occur as well. | No equivalent |
| 21 | Coniferous Cultivated Plantation (natural / planted) | Managed pine plantations, densely planted. Most planted stands are loblolly, but slash and longleaf occur as well. | No equivalent |
| 51 | Deciduous Cultivated Plantation | Planted deciduous trees. Includes sweetgum and sycamore plantations. | No equivalent |
| 36 | Successional Deciduous Forests | Regenerating deciduous trees with a shrub stature. Commonly dominated by sweetgum, tulip poplars and maples. | No equivalent |
| 517 | Hemlock Floodplain Forest | Alluvial forest with hemlock and/or white pine in mountains and western piedmont. Hydrology is generally temporarily to seasonally flooded. | Canada Hemlock Forest |
| 522 | Northern Hardwoods | High Elevation forests including yellow birch, American beech, and yellow buckeye. Includes forests with Hemlock and Yellow Birch. | Northern Hardwoods Forest, Boulderfield Forest |
| 525 | Appalachian Oak Forest | A variety of oak forest types including Black, White, Scarlet Oaks in dry to mesic situations. Includes forests historically co-dominated by American Chestnut. | High Elevation Red Oak Forest, Montane White Oak Forest |
| 526 | Appalachian Cove Forest | Mixed Mesophytic forests of the mountains. Includes tuliptree, basswood, yellow buckeye and surgar maple. This class is mapped to include cove forests dominated or co-dominated by hemlock. | Rich Cove Forest, Acidic Cove Forest |
| 527 | Appalachian Hemlock | Upland hemlock forests of the moutains region. Vary from side slopes to steep slope positions. | Canada Hemlock Forest |
| 533 | Appalachian Swamp Forest | Evergreen and deciduous forests with saturated hydrologies. This class may contain a variety of trees species, including hemlock - red maple, pitch pine, and white pine forests. | Swamp Forest-Bog Complex, Southern Appalachian Bog, Southern Appalachian Fen |
| 534 | Appalachian Wet Shrubland/ Herbaceous | Saturated shrubs and herbaceous vegetation. Often mapped as an inclusion in Appalachian Swamp Forest. | Southern Appalachian Bog, Southern Appalachian Fen |
|
Bent, A.C. 1953. Life histories of North American wood warblers. U.S. Natl. Mus. Bull. 203. Washington, D.C.
Hagan, J.M., III, and D.W. Johnston, editors. 1992. Ecology and conservation of neotropical migrant landbirds. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C. xiii + 609 pp. Simpson MB Jr. 1992. Birds of the Blue Ridge Mountains. Chapel Hill and London: University of North Carolina Press. Fussell, J. III and M. Lyons. 1990. Birds of the Outer Banks [pamphlet]. Eastern National Parks and Monument Association Coastal Wildlife Refuge Society. James, F.C., D.A. Wiedenfeld, and C.E. McCulloch. 1992. Trends in breeding populations of warblers:declines in the southern highlands and increases in the lowlands. Pages 43-56 in J.M. Hagan III and D.W. Johnston, editors. Ecology and conservation of neot Sauer, J.R., and S. Droege. 1992. Geographical patterns in population trends of neotropical migrants in North America. Pages 26-42 in J.M. Hagan III and D.W. Johnston, editors. Ecology and conservation of neotropical migrant landbirds. Smithsonian Institu Fussell, J.O. III. 1994. A birderís guide to coastal North Carolina. Chapel Hill and London: The University of North Carolina Press. Dunn, J.L., and K.L. Garrett. 1997. A field guide to warblers of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston. Nicholson CP. 1997. Atlas of the breeding birds of Tennessee. Knoxville: University of Tennessee Press. Harrison, C. 1978. A field guide to the nests, eggs and nestlings of North American birds. Collins, Cleveland, Ohio. Griscom, L., and A. Sprunt, Jr. 1979. The warblers of America. Doubleday and Co., Garden City, New York. 302 pp. Harrison, H.H. 1979. A field guide to western birds' nests. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston. 279 pp. Potter, E. F., J. F. Parnell, and R. P. Teulings. 1980. Birds of the Carolinas. Univ. North Carolina Press, Chapel Hill. 408 pp. Terres, J.K. 1980. The Audubon Society encyclopedia of North American birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York. American Ornithologists' Union (AOU), Committee on Classification and Nomenclature. 1983. Check-list of North American Birds. Sixth Edition. American Ornithologists' Union, Allen Press, Inc., Lawrence, Kansas. National Geographic Society (NGS). 1983. Field guide to the birds of North America. National Geographic Society, Washington, D.C. Raffaele, H.A. 1983. A guide to the birds of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands. Fondo Educativo Interamericano, San Juan, Puerto Rico. 255 pp. Harrison, H.H. 1984. Wood warblers' world. Simon and Schuster, New York. 335 pp. Ehrlich, P.R., D.S. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder's handbook:a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Shuster, Inc., New York. xxx + 785 pp. Ridgely, R.S., and G. Tudor. 1989. The birds of South America. Vol. 1. The Oscine passerines. Univ. Texas Press, Austin. 516 pp. Stiles, F.G., and A.F. Skutch. 1989. A guide to the birds of Costa Rica. Comstock Publ. Associates, Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York. 511 pp. Alsop FJ III. 1991. Birds of the Smokies. Gatlinburg: Great Smoky Mountains Natural History Association. Morimoto, D. C., and F. E. Wasserman. 1991. Dispersion patterns and habitat associations of rufous-sided towhees, common yellowthroats, and prairie warblers in the southeastern Massachusetts pine barrens. Auk 108:264-276. Ball, R. M., Jr., and J. C. Avise. 1992. Mitochondrial DNA phylogenetic differentiation among avian populations and the evolutionary significance of subspecies. Auk 109:626-636. |
For more information please contact them at:
NC-GAP Analysis Project
Dept. of Zoology, NCSU
Campus Box 7617
Raleigh, NC 27695-7617
(919) 513-2853
www.basic.ncsu.edu/ncgap