
| Taxa: |
| Order: |
| Family: |
| Reptilia |
| Squamata |
| Colubridae |
| NatureServe Global Rank: |
| NatureServe State (NC) Rank: |
| G5 |
| S4 |
| Federal Status: |
| NC State Status: |
| --- |
| --- |
| Land Unit |
| US Fish & Wildlife Service |
| US Forest Service |
| US National Park Service |
| US Department of Defense |
| NC State Parks |
| NC University System |
| NC Wildlife Res. Com. |
| NC Forest Service |
| NC Div. of Coastal Mgmt. |
| Local Governments |
| Non-Governmental Org. |
| Other Public Lands |
| Private Lands |
| GAP Status 1-2 |
| All Protected Lands |
| Statewide |
| Hectares |
| 15,699.96 |
| 142,235.82 |
| 70,919.64 |
| 24,635.07 |
| 21,538.44 |
| 2,895.75 |
| 52,355.43 |
| 4,149.45 |
| 265.14 |
| 3,009.87 |
| 5,186.52 |
| 4,070.07 |
| 6,399,510.93 |
| 102,081.51 |
| 343,961.82 |
| 6,746,472.09 |
| Acres |
| 38,795.44 |
| 351,472.30 |
| 175,246.21 |
| 60,874.57 |
| 53,222.63 |
| 7,155.55 |
| 129,373.06 |
| 10,253.51 |
| 655.18 |
| 7,437.55 |
| 12,816.17 |
| 10,057.36 |
| 15,813,532.82 |
| 252,248.86 |
| 849,948.00 |
| 16,670,892.35 |
| % of Dist. on |
| Prot. Lands |
| 4.6 % |
| 41.4 % |
| 20.5 % |
| 7.2 % |
| 6.3 % |
| 0.8 % |
| 14.9 % |
| 1.2 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 1.4 % |
| 1.4 % |
| 0.9 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 29.7 % |
| ----- |
| ----- |
| % of Dist. on |
| All Lands |
| 0.2 % |
| 2.1 % |
| 1.1 % |
| 0.4 % |
| 0.3 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 0.8 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| < 0.1 % |
| 94.9 % |
| 1.5 % |
| ----- |
| ----- |
|
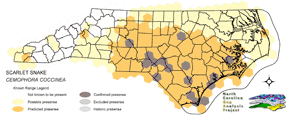
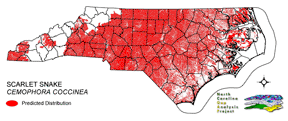
NATURE SERVE GLOBAL HABITAT COMMENTS: Hardwood, mixed, or pine forest/woodland and adjacent open areas with sandy or loamy well-drained soils (Behler and King 1979). Also salt grass prairie in Texas (Tennant 1984). Largely fossorial; sometimes found under rocks or in or under logs. Eggs are laid under moist humus (Minton 1972) or in other underground sites. |
| Code | Name | Description | NC Natural Heritage Program Equivalent |
| 121 | Maritime Pinelands | Loblolly forests and woodlands of the outer coastal plain. | Estuarine Fringe Loblolly Pine Forest |
| 63 | Coastal Plain Mesic Hardwood Forests | Beech dominated forests with white oak and northern red oak as possible co-dominants. Dry-mesic to mesic forests on slopes and small stream bottoms in the coastal plain. | Mesic Mixed Hardwood Forest, Basic Mesic Forests |
| 138 | Coastal Plain Dry to Dry-Mesic Oak Forests | Oak dominated forests of the coastal plain. Includes white oak forests with water oak or northern red oak and hickories as co-dominants. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Basic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 97 | Mesic Longleaf Pine | Longleaf pine woodlands without a major scrub oak component. Slash or loblolly pines may be present as well. | Mesic Pine Flatwoods |
| 42 | Xeric Longleaf Pine | Sandhills including a range of longleaf pine density from predominantly wiregrass, scrub oak dominated to true longleaf pine woodland. This does not include mesic or saturated flatwood types. | Xeric Sandhill Scrub, Pine/Scrub Oak Sandhill, Coastal Fringe Sandhill |
| 46 | Xeric Oak - Pine Forests | Mixed forest dominated by yellow pines with white or northern red oaks co-dominating. | Pine Oak Heath |
| 232 | Xeric Pine-Hardwood Woodlands and Forests | Mixed forest dominated by yellow pines with drier oaks including southern red, post, and chestnut oaks. | Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 228 | Piedmont Dry-Mesic Oak and Hardwood Forests | Primarily oak dominated forests, white oak is often dominant, with co-dominants including . Also represented by sweetgum and tulip poplar dominated forests. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Basic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 222 | Piedmont Dry-Mesic Pine Forests | Loblolly dominated forests resulting from succession following clearing. This type occurs on all moisture regimes following disturbance with the exception of the extremely xeric sites. | No equivalent |
| 382 | Dry Mesic Oak Pine Forests | Mixed forests of the coastal plain and piedmont. Includes loblolly pine with white, southern red and/or post oak and loblolly with water oak. On basic sites of the piedmont, eastern red cedar may co-occur with post, black, and blackjack oaks. | Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Xeric Hard Pan Forest, Chestnut Oak Forest, Dry Mesic Oak Hickory Forest, Dry Oak Hickory Forest |
| 220 | Piedmont Xeric Pine Forests | Dry to xeric pine forests dominated by Virginia pine, shortleaf pine or Eastern Red Cedar. | Pine Oak Heath |
| 226 | Piedmont Xeric Woodlands | Generally post and blackjack oak dominated woodlands. White ash and pignut hickory can be found in combination with Eastern red cedar on glades. | Xeric Hardpan Forest |
| 180 | Agricultural Crop Fields | Farm fields used for row crops. | No equivalent |
| 205 | Agricultural Pasture/Hay and Natural Herbaceous | Farm fields used for pasture grass or hay production, as well as old fields dominated by native and exotic grasses. | No equivalent |
| 202 | Residential Urban | Includes vegetation interspersed in residential areas. Includes lawns, mixed species woodlots, and horticultural shrubs. Vegetation accounts for between 20 - 70% of the cover. | No equivalent |
|
Dowling, H. G. 1993. Viewpoint:a reply to Collins (1991, 1992). Herpetol. Rev. 24:11-13.
Minton, S. A., Jr. 1972. Amphibians and reptiles of Indiana. Indiana Academy Science Monographs 3. v + 346 pp. Behler, J. L., and F. W. King. 1979. The Audubon Society field guide to North American reptiles and amphibians. Alfred A. Knopf, New York. 719 pp. Ashton, R. E., Jr., and P. S. Ashton. 1981. Handbook of Reptiles and Amphibians of Florida. Part One:The Snakes. Windward Pub. Co., Miami, Florida. 176 pp. Williams, K. L. 1985. CEMOPHORA, C. COCCINEA. Catalogue of American Amphibians and Reptiles 374:1-4. Tennant, A. 1984. The Snakes of Texas. Texas Monthly Press, Austin, Texas. 561 pp. Collins, J. T. 1991. Viewpoint:a new taxonomic arrangement for some North American amphibians and reptiles. SSAR Herpetol. Review 22:42-43. |
For more information please contact them at:
NC-GAP Analysis Project
Dept. of Zoology, NCSU
Campus Box 7617
Raleigh, NC 27695-7617
(919) 513-2853
www.basic.ncsu.edu/ncgap